pull/ push system
a pull system(수요에서 부터 당기는 거고) starts with demand from customer.
in push system, all forecasting and other decision are made centrally. stock pushed out into the system from central supply. field warehouse have little of no say in what they receive.
the detail of pull system
pull system starts with demand from a customer and signals each preceding operation. work is not done on a product unless a signal for demand is generated, thus pulling a product through the manufacturing process.
pull system + JIT
In a Just In Time systme of manufacturing, a work center will provide the previous work center with a signal to 'pull' more materials. this method allows the manufacturing system to produce more closely to demand, reducing dramatically the inventory levels needed.
Pull system + periodic review systme
pull system + kanbansystem
in pull system, the preceding operation does not produce anything unless a signals sent from the following operation to do so. the most well known system is the kanban system and it is basically a two bin system; when one bin is used up, it is sent back to the supplier operation and is the signal forward to the customer.
the advantage of push system.
the advantage of push systme in distribution is replenishment decision making is centralized usually at the manufacturing site or central supply facility.
in push system, all forecasting and other decision are made centrally. stock pushed out into the system from central supply. field warehouse have little of no say in what they receive.
backward/forward scheduling
backward scheduling ( 뒤에서 부터)
backward scheduling schedules the last operation on the routing so that the completion date is the due date.
all previous operation are scheduled back from the last operation.
the benefit of backward scheduling is that it schedules back from the customer due date. however, there is no slack time, on time delivery and service may suffer.
forward scheduling (order date 부터 앞으로 센다)
forward scheduling assumes that material are not ordered and operation are not scheduled until the customer order is received, regardless of the due date. = forward scheduling assumes the material procurement and operation scheduling for a component starts when the order is received whatever the due date, and that operations are scheduled forward from this date = when the order is received.
forward scheduling + make to order(FM으로 외우자)
in a make to orde enviorment, work does not begin until the order is received from the customer. the order is then scheduled forward from the order date and considers the load on the finite capacity of each work center through which the order must move.
how to calculate the scheduling date for forward scheduling
forward scheduling begins when the order is received. the due date for the customer would be calculated based on material purchases and operating scheduling. it is used for developing promise date for the customer of determining whether a date order can be deivered on time.
flow system
in the flow system, workstations are designed to produce a limited range of similar products, and there is very little buildup of WIP inventory. bacause in their purest form, flow line are inflxible.
in the flow system, workstations are designed to produce a limited range of similar products, and there is very little buildup of WIP inventory. because in their purest form, flow lines are inflxible. they can produce only a limited family of similar parts and the quantity must be sufficient to justify economically it use.
Stock Location -floating location system/ fixed location system.
a floating location system - 최신 데이터를 반영한 시스템이 꼭 필요함
the advantage of floating location system.
this system improved cube utilization/
the characteristic of floating location system
this system requires accurate and up to date information on item location.
a fixed location system -system이 필요 없을 정도고
the advantage of fixed location system.
this system makes it possible to store and retrieve items with a minimum of record kepping in some small, manual systems, no records are kept at all.
in fixed location, an SKU is assigned a permanent location and no other items are stored there.
the disadvantage of fixed location system.
the warehouse having a fixed location offers poor cube utilization becuase pallet location are left empty when the product assigned to the the location is out of stock. generlly, fixed locations are used in small warehouses with low throughput.
the characteristics of fixed location systme.
in fixed position layout, resource are portable and come to the job site to perform acticities. so it can avoid the high cost of moving the product from one workstation to another.
planning bill - one of bill of material structures.
the definition of planning bill
a planning bill is an artificail grouping of components for planning purposes ( they do not represent product which are buildable) = planning bill are bills of material which represent average products.
they are used to simplify planning, forecasting, master production scheduling, and material requirement planning.
Available To Promise
in make to order or assemble to order enviorments, demand is satisfied from production capacity. since demand can be satisfied either from inventory or from scheduled receipts, the MPS provides a plan for doing either. as order are received, they consume the available inventory or capacity. any part of the plan that is not consumed by actual customer order is Available To Promises to customers. in this way, the MPS provides a realistic basis fro making delivery promises.
using MPS, sales and distribution can determine the available to promise(ATP). Available To Promise is that portion of a firm's inventory and planned production that is not already committed and is available to customer. this allows delivery promises to be made and customer orders and deliveries to be scheduled accurately.
the ATP is calculated by adding scheduled receipts to the beginning inventory and then substracting actual order scheduled before next shcedule receipt.
the defination of available to promist
1) the portion of a company's inventory and planned production which is not alreay commited is available to promise.
2) available to promise is the portion of inventory and planned production not already commited to orders. it allows accurate delivery promises to be made to the customer.
3) available to promise is the part of inventory and planned production which is available to be promised to customers for delivery(= not commited). it calculated by adding scheduled receipts to the beggining inventory and substracting actual order scheduled before the next scheduled receipt.
Production Plan - MPS - MRP
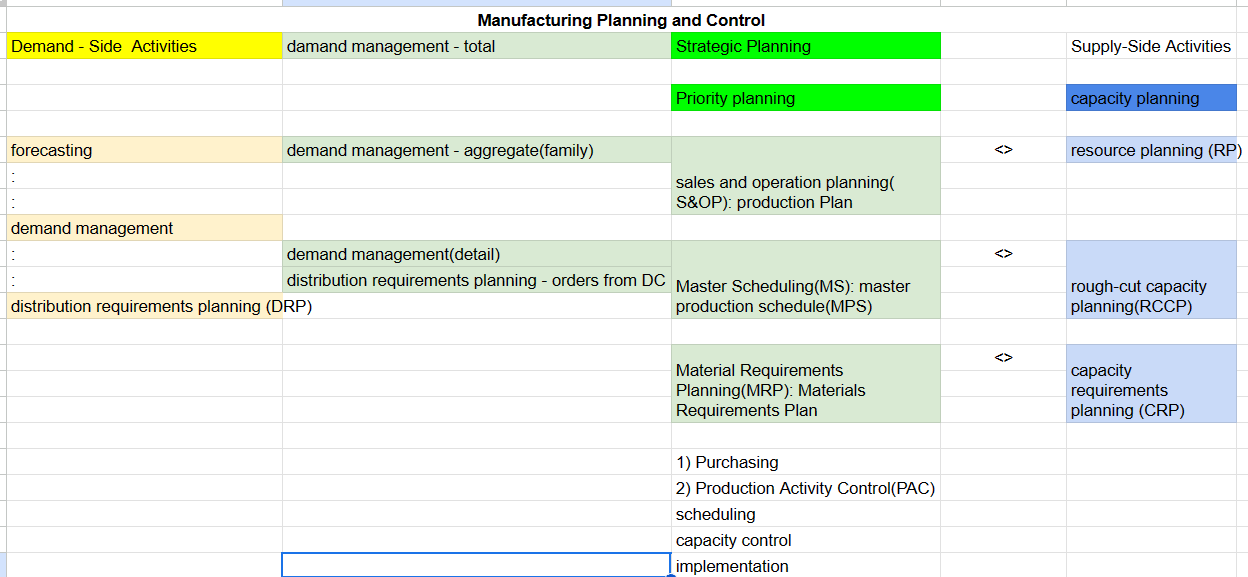
Sales & Operation (S&OP)
- the sales ans operation planning is done at the level of product family (group).
- the sales and operation planning brings together all the plans for the business(sales, marketing, development, manufacturing, sourcing, and financial) into one integrated plan.
- it is performed at least one a month and is reviewed by management at an aggregated(product family) level.
MPS(Master Production Schedul)
the definition of MPS
the master production schedule is the planned(anticipated) build schedule for manufacturing. a final assembly schedule is generally seperate from the MPS and the actual build schedule may vary from what was planned.
the objective of establishing MPS are following;
the master scheduler, when developing the MPS, must make sure labor, material, equipment, and inventory are being used efficiently in order to maintain high level of customer service. efficient final assembly would be developed by a final assembly schedule.
- efficeint use of resource
- high customer service levels
- efficient use of inventory
the characteristics of MPS
- the master production schedule, once established, is submitted to the MRP system for use in calculating demand for the component.
- the mps is used to faciliate communication between sales and manufacturing.
- the MPS is a weekly build plan that contains more detail than the production plan. however, the MPS shoud add up to equal the production plan.
the steps in developing a master production schedule(MPS)
there are three steps in developing a master production schedule ;
- develop a preliminary MPS
- check the preliminary MPS against availavle capacity.
- resolve difference between the preliminary MPS and capacity available.
the inputs to realistic MPS are;
- production plan
- forecasts for end items
- capacity constraints
- while costs are nice to have, they are not a nessary input.
MPS & rough- cut -capacity planning
rough-cut-capacity planning can be describes as checking to be sure that critical resources are available to support the preliminary MPS. rough-cut-capacity planning is concerned with making sure that critical resources are available at the preliminary MPS stage before committing to the schedule. critical resources are bottleneck operations(not every work center), labor and material which may be scarce or have long lead time.
MPS & Production Planning(production plan)
production planning is generally a direct input to master production scheduling. production planning are agreed upon management plans for manufacturing, shipping and inventory/backlog(ood). these plan are developed at the aggregate level( e.g. monthly, product families). the plan provides management approval for the master scheduler to develop the detailed master schedule(end products, weekly)
MRP(Material Requirements Planning)
the definition of MRP
the role of MPS is showing the end items, or major components, that manufacturing intends to build. these items are made or assembled from components that must be available in the right quantities and at the right time to meet the MPS requirements. material requirements planning is the system used to avoid missing parts. it establishes a schedule(priority plan) showing the components required at each level of the assembly and based on lead times, calculate the time when these components will be needed.
the major objectives of MRP
MRP has two major objectives;
- determine requirements
- keep priorities current
Inputs to the material requirement planning system are
MPS drives the MRP system by providing the initial input for the items needed. a major input to the MRP is inventory. when a calculation is made to find out how many are needed, the quantities available must be considered. the BOM shows all the part required to make one of them.
- MPS
- Inventory records
- BOM
MRP & MPS
the master production schedule, once established, is submitted to the MRP system for use in calculating demand for the components.
MRP & CRP
1) what is CRP?
- CRP is capacity requirements planning.
- is capacity planning at a more detailed level and is direcly linked to the material requirements plan
- is concerned with individual orders at individual work center and calculates work center loads and labor requirements for each item period at each work center.
- noted that althorugh the upper levels of priority planning are input to lower level, the various capacity plans related only to their level in the priority plan, not to subsquent capacity planning levels.
2) relationship with MRP and CRP
the input needed for CRP are open shop order, planned order in MRP, routing, time standard, leadtimes, and workcenter capacities.
Closed-loop MRP
- if the priority plans have to be adjusted at any planning levels because of capacity problems, those should be reflected in the levels above. thus there must be feedback throughout the systme so that planning can be kept valid at all times.
- closed-loop MRP is a system built around MRP that includes the additional planning functions of SOP, MRP, CRP, purchasing , PAC.
- the term closed loop implies not only that each of these elements is included in the overal system, but also that feedback is provided by the execution functions so that plant.
- a closed loop MRP defined as integrated planning and control system with feedback from the bottom-up.
- closed loop MRP system operate from the top down with feedback throughout the system. these feedback mechanism allows changes to occur in the top level planning.
MRP& Pegging data
in MRP, the process of using pegging data to solve material availabiltiy or other problem. this process is accomplished by the partner. potential solutions include compressing LT, cutting order quantity, substituing material, and changing the master schedule.
MRP & low-level code
- a low level code is defined as lowest level on which a part resides in the BOM.
- the low level code tells the MRP system the lowest level in which the part resides. the system uses this information to determine when to total all the requirements for a components the end item is the 0 level.
where used report(parent)/ pegging report(parent for which there is existing demand requirements)
the definition of a where-used report
a where-used report provides all list of all parent where a component is used. it is usefull for making mass component.
where-used report & bill of material
where-used report gives the same information as bill of material, but the where-used report gives the parent for a component whereas the bill gives the componenets for a parent. a componenet may be used in making several parents. wheels on an automobile, for example, might be used on several models of cars. a listing of all the parents in which a component is used is called a where-used repot. this has several uses, such as in implementing an engineer change of when materials are scares or in costing a product.
where-used report & pegging report(used to trace the origin of demand for a component. it shows the parent for which demand exist)
a pegging report is similar to a where-used report. however, the pegging report shows only thoese parent for which there is existing demand requirement, whereas the where-used report shows all parents for components. the pegging report shows the parents creating the demand for the components, the quantities needed and when they are needed.
pegging keeps track if the origin of the demand. a pegging report is used to trace the origin of demand for a component.
it shows only the parent for which demand exist, unlike the where-used report which shows every parent in which a component is used.
time zone - liquid , slushy, frozen zone
the liquid zone
the time fence zone known as the liquid zone would have the following characteristics.
any change can be made to the MPS within the production plan.
the liquid zone is characterized by mostly forecast orders and changes can reaily be made without an impact to the bottom line.
the slushy zone
the slushy zone usually requires negotiated trade-offs between marketing and manufacturing.if capacity is available, then change can usually be made.
periodic review system
the definition of periodic review system
makes the timing of each order a regular interval. using the pereodic review system, the quantity on hand of a particular items is determined at specified, fixed time intervals and an order is placed.
thus the review period is fixed, and the order quantity is allowed to vary. the quantity on hand plus the quantity ordered must be sufficient to last until the next shipment is received.that is the quantity on hand plus the quantity ordered must equal the sum of the demand during the lead time plus the demand during the review period plus the safety stock.
the characteristics of period review system.
in periodic review system, the order is placed everytime units and order quantity is variable.
the period review system makes the timing of each order a regular interval.
under the following conditions, a periodic review system (supermarket) is the most effective method to manage inventory.
- small issues from inventory and transaction are expensive
- order costs are small
- many items are ordered together.
period review system & target-level or maximum-level inventory.
the quantity equal to the demand during the lead time plus the demand duting the review period plus safety stock is called the target-level or maximum-level inventory.
bias / MAD/ forecast/ tracking signal
bias&forecast &tracking signal
bias occurs when actual demand varies consistently higher or lower thant the forecast. when bias occurs in the forecast, the forecast must be adjusted. tracking signal detects bias in a forecast.
bias(whether error exist to adjust the forecast)&MAD(if yes, how much error exist to compensate for)
- the MAD express the size of the average error irrespective of whether it is positive of negative. it's the combination of bias and MAD that allow us to evalutate forecasting results.
- bias is perhaps the most critical, since we can compensate for forecast errors through safety stock, expediting, faster deivery means. MAD indicates the expected compensation's size.
- the best-known measure of deviation or dispersion from statistics is the standard deviation. when error are disrupted normally, standard deviation of forecast is 1.25 MAD. bias and tracking signals have the tendency of the forecast to be either above or below the actual observation.
- to sum up, bias occurs when actual demand varies consistently higher or lower than the forecast. when bias occurs in the forecast, the forecast must be adjusted. tracking signal detect bias in a forecast.
- tracking signal are used to measure the qualtiy of the forecast to determine whether to adjust the forecast. they usually mearsure the sum of error against a deviation measure such as MAD.
total quality control
- total qualtiy control is if defects are discoverd, the process should be stopped.
- ultimately the company's user is customer and also the next operation in the process. daily monitoring can best be done by the operator. if defects are discovered, the process should be stopped and the cause of the defects corrected.
cube utilization.
cube utilization & floating location system.
the advantage of floating location system is this system improved cube utilization(적재 공간의 활용).
the balance to cube utilization is accessibility
cube utilization must alway be balanced with accessibility to the goods when they are needed. for example, a ware house could have 100 percent cube utilization byt the warehouse pickers could not pick the goods. therefore, warehouses do not operate at 100% cube utilization.
cube utilization & fixed location warehouse
fixed location warehouses offer poor cube utilization because pallet location are left empty when the product assigned to the location is out of stock. generally, fixed locations are used in small warehouses with low throughput.
chase strategy, level strategy
- chase strategy and level strategy are one of the strategies to use in developing a production plan.
- the chase strategy means production will vary with demand(inventory stays level)
- the level strategy establishes production at the average demand. fluctuation in demand are absorbed by inventory.
- the third strategy is subcontracting. production is kept at the minimum demand level. variateion in demand are absorbed by subscontracting.
lot for lot
- orderd only amount required.
- used for dependent demand items.
- used in JIT enviorment.
lot for lot sizing technique that generates planned order in quantities equal to the net requirement in each period.
since items are ordered only when needed this system creastes no unused lot-size inventory. because of this, it is used for expensive components.
point of use inventory
it is one of the types for storage in production facility. one of them is central location, which have a facility only for storing the materials. whereas, in case of point-of-use inventory, there is no need to handling the material. also they manage the material only having the stock issue. the primary benefit of point of use inventory is reduce material handling.
C type would be most applicable.
income statement/ balance sheet
- income statement shows revenue, expense, and income(profit)
- revenue comes from the sale of goods or service
- expenses come from the cost of goods sold and the general and administrative expense.
- cost of goods sold include direct labor, material and overhead whereas general and administrative.
- expense include advertising, insurance, taxes, etc.
- profit comes from revenue minus expense.
- the balance sheet for a firm shows
- profit or loss for the period
- short term debt
- cost of product sold
the role of warehouse serve
- transportation consolidation - consolidate small shipment(LTL) into large shipment(TL)
- product mixing - group a variety of products into one order.
- customer service - allows products to be placed closer to the customer
- inventory will typically rise with an increas in the number of warehouse.
decentralized/ centralized distribution system
in decentralized distribution systme, the role of the central supply organization is to respond to demands from the distribution centers.
cost of ordering / cost of carrying inventories
- cost of ordering
- production control cost
- setup and tear down cost
- lost capacity cost(ordering에 쓴 capacity를 잃는 것)
- purchase order cost
- cost of carrying inventory
- capital cost
- storage cost
- risk cost(obsolescene, damage, pilferage, deterioratoin)
- opportunity cost*
*the most significant cost factor that contributes to inventory carrying cost is opportunity cost.
- 기타
- shop packet
- manufacturing order, operation sheet, engineering blue print, packing list 등 작업장 을 운영하는 데 필요한 서류 들의 뭉치
- Routing은 작업 절차서임
- shop packet
\
- work-in precess inventory
- work-in pocess inventory serves to decouple an operation form succeding operation.
- net requirement
- material requirement planning scheduls a planned order receipt when a net requirement exists.
- lot for lot sizing technique that generates planned order in quantities equal to the net requirement in each period.
- net requirements = gross requirements - scheduled receipts - available inventory
- transportation - water, truck
- low level code
- planner / buyer
- EOQ
- JIT TQM
- unitlization
- production plan
- intermittent manufacturing
- exponential smoothing
- scrap rate - how to evaluate the performance of supplier
- blanket order
- product layout
- system nervousness- firm planned order
- fluctuation demand/ hedge demand/
- owner's equity
- make to order
- mixed model production
- total employee involvement
- capacity requirement planning
- quick setup and changeover
- ABC appoach
- rough cut capacity
- conformation
- work center ;pad re[prt
- CRP
- in order to manage quest and lead time, input/output control is used.
- dispatching
- cycle counting
- shop calendar
- bottleneck
- bill of material
- continous production process
- periodic review system
- exception message
- back order/back log
- BOM
- PAC
- a characteristic of a product focused layout is fixed flow of work.
- service part include independent material
- overload work centers determines the throughtput of a manufactuting process
- backflushing
- offsetting/expliding
- quality must be the operator's responsibility. they are the only one who can make sure defects are not built into the product . they must be allowed to stop prcess when defects are found.
- periodic review systme
- input/output control is measured in hours
- the most critical in achieving the goal of value added is the materials and labor is the least important usually.
- a characteristic of a product focused lay out is fixed flow of work.
'스터디스터디 > CPIM' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [summary]16. Total quality management (0) | 2023.10.15 |
|---|---|
| Pocket Prep - part 1 (1) | 2023.03.28 |
| 350제 - 계산문제 (0) | 2023.03.24 |
| 350제 - 헷갈린거 정리 (0) | 2023.03.24 |
| [Completed]350제 - 4 (0) | 2023.03.24 |
